Loadbalancing with metallb for my bare-metal cluster
Now that we have k3s installed and our nodes communicating over the tailnet, we need a way to access the services running in my cluster.
Metallb
MetalLB is a load-balancer implementation for bare-metal Kubernetes clusters, using standard routing protocols.
In short, it allows you to create Kubernetes services of type LoadBalancer in kubernetes clusters that don’t run on a cloud provider, such as bare-metal clusters.
Installing the controller
Head over to the installation docs. I personally chose to install by manifest, which creates a metallb-system namespace for us.
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.13.7/config/manifests/metallb-native.yaml
Metallb runs as a daemonset, creating a pod that runs on each node known as speaker, in addition to a controller. The controller will handle assinging IPs to services, while each speaker will advertise services with assigned IPs using the strategy configured. I currently have 3 nodes in my cluster there are 3 speakers total.
$ kubectl get daemonset -n metallb-system
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
speaker 3 3 3 3 3 kubernetes.io/os=linux 5h30m
$ kubectl get pods -n metallb-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
controller-84d6d4db45-zvd2d 1/1 Running 0 5h22m
speaker-xmngr 1/1 Running 0 5h22m
speaker-sqrsq 1/1 Running 0 5h22m
speaker-gf2cm 1/1 Running 0 5h22m
Configuration
We need to tell metallb what ip pool it has to pick from. You can use 10.0.1.0/24 syntax here or a range such as 10.0.0.0-10.0.0.100. To do this, we create an IPAddressPool.
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: IPAddressPool
metadata:
name: load-balancer
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
addresses:
- 10.0.1.0/24
Next, we tell metallb how we want to advertise our services.
apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1
kind: L2Advertisement
metadata:
name: l2advertisement
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
ipAddressPools:
- load-balancer
Run a kubectl apply to your metallb namespace for your address pool and advertisement configs.
Tailscale
Check out tailscales kb article on subnets and why you want to use them.
I want to access services metallb advertises in my tailnet, which is a good use case for a subnet router.
Subnet Routers
I am advertising the 10.0.1.0/24 CIDR for my subnet router. This means we will be able to access any ip address in that range from devices that are connected to my tailnet, even if we I am not connected to the same local network. This only needs to be done on whichever node you want to use as a subnet router.
NOTE: The ip range that you gave metallb to use need to fall under the CIDR for your subrouter. If you’re unsure, check out https://www.ipaddressguide.com/ to verify your ip range is correct.
We’ll need to choose a machine to act as our subnet router and rerun tailscale up advertising the routes we want to expose to the tailnet.
sudo tailscale up --advertise-routes=10.0.1.0/24
Approving our Subnet Router
Once you’ve ran some flavor of sudo tailscale up, navigate over to your tailnet admin console.
Lets approve our subnet and disable key expiry. I’ve already disabled key expiry for this particular machine. Subnet routes can be approved under edit route settings.
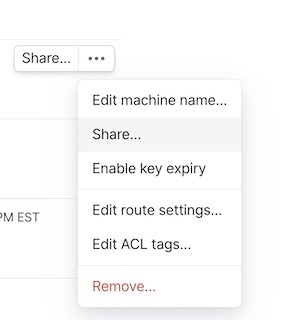
Approve your subnet route(s)
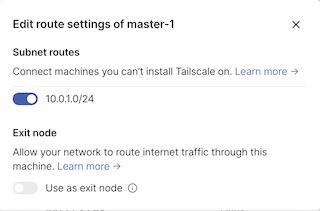
Our subnet router should be ready to use!
Testing out metallb & tailscale subnet router
To test out our new setup, we’re going to deploy pihole to our cluster, have metallb assign it an external ip, and use it to do a dns lookup for google.com.
Pihole
Pi-hole is a general purpose network-wide ad-blocker that protects your network from ads and trackers without requiring any setup on individual devices. You can also use it as a DNS server.
Defining our pihole deployment
Check out these helm charts for setting up your deployment.
Lets create a namespace for pihole to live in.
$ kubectl create namespace pihole
Next, let’s take a look at the services we are going to deploy.
Pihole homelab-pihole-dns-tcp and homelab-pihole-dns-udp will be the services used for dns lookups.
Take note of the annotations on each of these two services. metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs tells metallb what ip(s) you want to assign to this service. Make sure the IP you assign to the services is within the range you gave metallb in the IPAddressPool.
Because homelab-pihole-dns-tcp listens on TCP and homelab-pihole-dns-udp listens on UDP, these two services can share the same IP address.
The annotation metallb.universe.tf/allow-shared-ip tells metallb to allow this. Each service that will be sharing an IP is required to have the annotation.
PiHole Services YAML
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-dns-tcp
labels:
app: pihole
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/allow-shared-ip: shared-pihole-dns
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 10.0.1.70
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- port: 53
targetPort: dns
protocol: TCP
name: dns
selector:
app: pihole
release: homelab
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-dns-udp
labels:
app: pihole
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/allow-shared-ip: shared-pihole-dns
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 10.0.1.70
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- port: 53
targetPort: dns-udp
protocol: UDP
name: dns-udp
selector:
app: pihole
release: homelab
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-web
labels:
app: pihole
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 10.0.1.71
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: http
protocol: TCP
name: http
- port: 443
targetPort: https
protocol: TCP
name: https
selector:
app: pihole
release: homelab
Here is the full yaml I am using. You can leave out the custom dnsmaq config map and remove the volume from the deployment. We will be covering those in a later post.
Full PiHole Kubernetes YAML
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-password
labels:
app: pihole
chart: pihole-2.11.1
heritage: Helm
release: homelab
type: Opaque
data:
password: "Y2hhbmdlLW1l"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-custom-dnsmasq
labels:
app: pihole
chart: pihole-2.11.1
release: homelab
heritage: Helm
data:
02-custom.conf: |
addn-hosts=/etc/addn-hosts
addn-hosts: |
05-pihole-custom-cname.conf: |
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-dns-tcp
labels:
app: pihole
chart: pihole-2.11.1
release: homelab
heritage: Helm
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/allow-shared-ip: shared-dns
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 10.0.1.70
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- port: 53
targetPort: dns
protocol: TCP
name: dns
selector:
app: pihole
release: homelab
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-dns-udp
labels:
app: pihole
chart: pihole-2.11.1
release: homelab
heritage: Helm
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/allow-shared-ip: shared-dns
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 10.0.1.70
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- port: 53
targetPort: dns-udp
protocol: UDP
name: dns-udp
selector:
app: pihole
release: homelab
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole-web
labels:
app: pihole
chart: pihole-2.11.1
release: homelab
heritage: Helm
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 10.0.1.71
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: http
protocol: TCP
name: http
- port: 443
targetPort: https
protocol: TCP
name: https
selector:
app: pihole
release: homelab
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: homelab-pihole
labels:
app: pihole
chart: pihole-2.11.1
release: homelab
heritage: Helm
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: pihole
release: homelab
template:
metadata:
annotations:
checksum.config.adlists: 01ba4719c80b6fe911b091a7c05124b64eeece964e09c058ef8f9805daca546
checksum.config.blacklist: 01ba4719c80b6fe911b091a7c05124b64eeece964e09c058ef8f9805daca546
checksum.config.regex: 01ba4719c80b6fe911b091a7c05124b64eeece964e09c058ef8f9805daca546
checksum.config.whitelist: 01ba4719c80b6fe911b091a7c05124b64eeece964e09c058ef8f9805daca546
checksum.config.dnsmasqConfig: 622ac6ff4c980b4443e393f5251d8190a29a0c471c3f1ddeeebaaee554fbf67
checksum.config.staticDhcpConfig: 01ba4719c80b6fe911b091a7c05124b64eeece964e09c058ef8f9805daca546
labels:
app: pihole
release: homelab
spec:
dnsPolicy: None
dnsConfig:
nameservers:
- 1.1.1.1
- 8.8.8.8
hostname:
hostNetwork: false
containers:
- name: pihole
env:
- name: 'WEB_PORT'
value: "80"
- name: VIRTUAL_HOST
value: pi.hole
- name: WEBPASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: password
name: homelab-pihole-password
- name: 'PIHOLE_DNS_'
value: '1.1.1.1;8.8.8.8'
image: "pihole/pihole:2023.01"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
securityContext:
privileged: false
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: http
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 53
name: dns
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 53
name: dns-udp
protocol: UDP
- containerPort: 443
name: https
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 67
name: client-udp
protocol: UDP
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /admin/index.php
port: http
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 60
failureThreshold: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /admin/index.php
port: http
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 60
failureThreshold: 3
timeoutSeconds: 5
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/pihole
name: config
- mountPath: /etc/dnsmasq.d/02-custom.conf
name: custom-dnsmasq
subPath: 02-custom.conf
- mountPath: /etc/addn-hosts
name: custom-dnsmasq
subPath: addn-hosts
- mountPath: /etc/dnsmasq.d/05-pihole-custom-cname.conf
name: custom-dnsmasq
subPath: 05-pihole-custom-cname.conf
resources:
{}
volumes:
- name: config
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pihole
- configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: homelab-pihole-custom-dnsmasq
name: custom-dnsmasq
You can check that your services got created. Note the external-ips that got assigned to our services. The dns services should be sharing whatever ip you gave them, and the pihole-web service should have its own ip.
$ kubectl get svc -n pihole
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
homelab-pihole-dns-tcp LoadBalancer 10.43.75.7 10.0.1.70 53:32441/TCP 20h
homelab-pihole-dns-udp LoadBalancer 10.43.242.253 10.0.1.70 53:30206/UDP 20h
homelab-pihole-web LoadBalancer 10.43.123.96 10.0.1.71 80:31059/TCP,443:31284/TCP 20h
And the pihole pod running
$ kubectl get pods -n pihole
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
homelab-pihole-989bd4c59-k9gd7 1/1 Running 0 19h
Validation
From my local laptop that is connected to the tailnet, I should be able to use the dns services to lookup domain names. We can use dig to test this out. If you’re on windows, you can use nslookup instead.
$ dig @10.0.1.70 google.com
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> @10.0.1.70 google.com
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 17033
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 6, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1232
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;google.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
google.com. 150 IN A 142.250.123.101
google.com. 150 IN A 142.250.123.100
google.com. 150 IN A 142.250.123.138
google.com. 150 IN A 142.250.123.102
google.com. 150 IN A 142.250.123.139
google.com. 150 IN A 142.250.123.113
;; Query time: 35 msec
;; SERVER: 10.0.1.70#53(10.0.1.70)
;; WHEN: Thu Feb 16 10:51:32 EST 2023
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 135
You can also navigate to the pihole dashboard from your browser
Tailnet wide ad blocking
If you’re interesting in getting ad blocking for any device connected to your tailnet via PiHole, you can configure tailscale to use your cluster pihole deployment.
Navigate over to the DNS page in your tailnet and add a custom nameserver. We’ll want to add the external-ip metallb assigned to the pihole services.
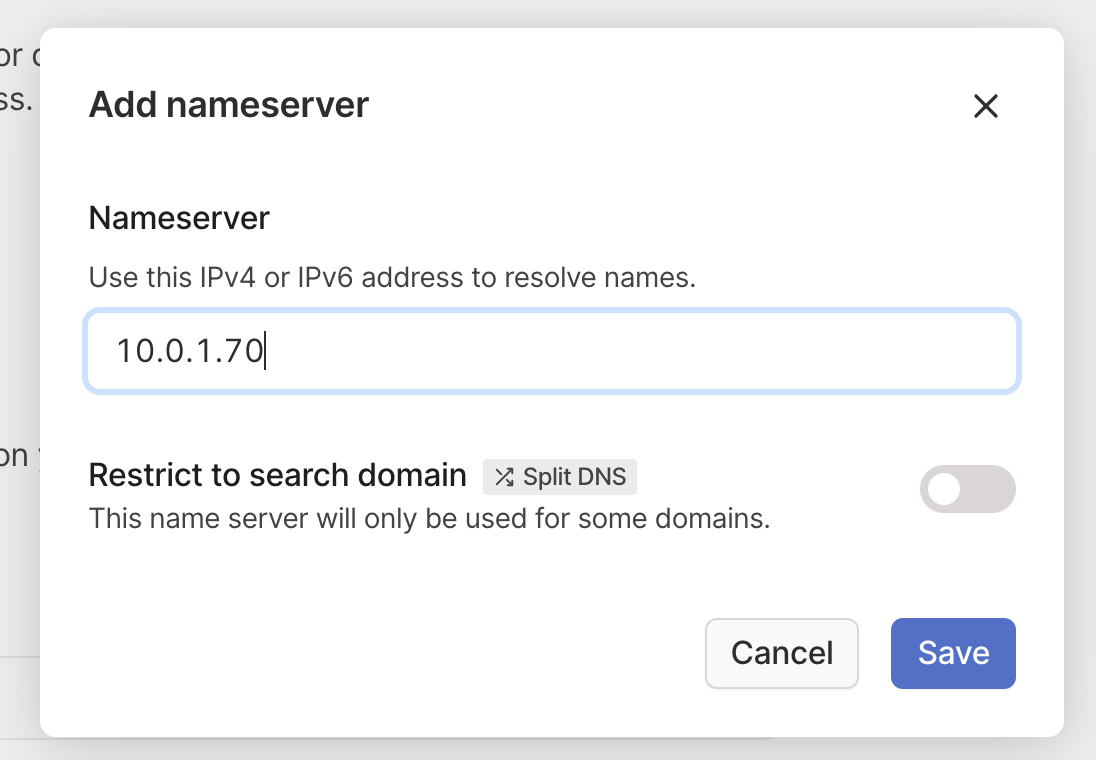
Enable local DNS override.

Now any device on your tailnet gets the benefit of pihole adblocking while connected.
NOTE: If your pihole services are down you are going to run into trouble with DNS lookups. You may want to consider a backup here or make sure your pihole services are highly available.